Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Koyamada, Koji*; Yu, L.*; Kawamura, Takuma; Konishi, Katsumi*
International Journal of Modeling, Simulation, and Scientific Computing, 12(2), p.2140001_1 - 2140001_19, 2021/04
With the improvement of sensors technologies in various fields such as fluid dynamics, meteorology, and space observation, it is an important issue to derive explanatory models using partial differential equations (PDEs) for the big data obtained from them. In this paper, we propose a technique for estimating linear PDEs with higher-order derivatives for spatiotemporally discrete point cloud data. The technique calculates the time and space derivatives from a neural network (NN) trained on the point cloud data, and estimates the derivative term of the PDE using regression analysis techniques. In the experiment, we computed the error of the estimated PDEs for various meta-parameters for the PDEs with exact solutions. As a result, we found that increasing the hierarchy of NNs to match the order of the derivative terms in the exact solution PDEs and adopting L1 regularization with LASSO as the method of regression analysis increased the accuracy of the model.
Aritomo, Yoshihiro*; Amano, Shota*; Okubayashi, Mizuki*; Yanagi, Baku*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Ota, Masahisa*
Physics of Atomic Nuclei, 83(4), p.545 - 549, 2020/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Physics, Nuclear)Uechi, Schun*; Uechi, Hiroshi*; Nishimura, Akihiko
World Journal of Engineering and Technology, 7(4), p.559 - 571, 2019/11
A water drinking bird is discussed in terms of a thermomechanical model. A mathematical expression of motion derived from the thermomechanical model of a drinking bird and numerical solutions are explicitly shown, which is helpful in understanding physical meanings and fundamental difference between mechanical and thermomechanical periodic motion. The mathematical and physical differences between mechanical and thermomechanical periodic motion. The process of a drinking bird motion could be applied to energy harvesting technology by way of the current modeling.
Kido, Kentaro
Journal of Computational Chemistry, 40(24), p.2072 - 2085, 2019/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:13.02(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Onizawa, Takashi; Hashidate, Ryuta
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 6(1), p.18-00477_1 - 18-00477_15, 2019/02
Aiming at enhancing its economic competitiveness and reducing radioactive waste, JAEA has proposed an attractive plant concept and made great efforts to demonstrate the applicability of some innovative technologies to the plant. One of the most practical means is to extend the design life to 60 years. Accordingly, the material strength standards set by JSME have to be extended from 300,000 to 500,000 hours but this extension requires more precise estimation of creep rupture strength and creep strain of the materials in the long term. This paper describes the development of creep property equations of 316FR stainless steel and Mod.9Cr-1Mo steel considering changes in creep mechanisms at high temperatures in the long term based on evaluations of long-term creep properties of the materials. The creep property equations developed in this study will provide more precise estimation of the creep properties in the long term than the present creep property equations of JSME.
Shen, X.*; Schlegel, J. P.*; Hibiki, Takashi*; Nakamura, Hideo
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 333, p.87 - 98, 2018/07
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:34.62(Nuclear Science & Technology)Shen, X.*; Sun, Haomin; Deng, B.*; Hibiki, Takashi*; Nakamura, Hideo
International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow, 67(Part A), p.168 - 184, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:62.14(Thermodynamics)An experimental study on upward bubbly air-water flows in a vertical large-diameter square duct have been performed by mainly using four-sensor probes. Local measurements of interfacial area concentration (IAC), void fraction, 3D bubble velocity vector and bubble diameter at 3 axial positions were conducted. Although the interfacial area transport equation (IATE) and its bubble coalescence and breakup models have already played an important role in predicting the IAC in general two-phase flow fields, they are mainly developed based on the two-phase flow experimental data taken in round pipes or small diameter channels. To confirm their usability in large-diameter square duct, this study has evaluated the 1D one-group IATE with its 6 sets of bubble coalescence and breakup models with the presently-obtained database. It was found the relative error between the best prediction and the database was 25%.
Shen, X.*; Schlegel, J. P.*; Hibiki, Takashi*; Nakamura, Hideo
Proceedings of 2017 Japan-US Seminar on Two-Phase Flow Dynamics (JUS 2017), 6 Pages, 2017/06
Fukui, Katsunori*; Hashiba, Kimihiro*; Matsui, Hiroya; Kuwabara, Kazumichi; Ozaki, Yusuke
JAEA-Research 2016-014, 52 Pages, 2016/09
With respect to high-level radioactive waste disposal, knowledge of the long-term mechanical stability of shafts and galleries excavated in rock is required, not only during construction and operation but also over a period of thousands of years after closure. On the other hand, it is known that rock and the rock mass surrounding the disposal gallery shows time dependent behavior such as creep or the stress-relaxation. It becomes the issue in the stability evaluation of the disposal gallery to grasp the behavior. In order to solve this issue, we pushed forward research development. we pushed forward research development. In the fiscal year of 2015, the creep testing machine for Tage tuff was moved to the new building. The creep test was continuously conducted and the total testing time exceeded 17 years. The testing equipment and procedure were examined to investigate the deformation, failure and time-dependency of rock under wet conditions and between room temperature and 100 C. The long-term strength of rock under triaxle stress state was researched with the aid of laboratory testing results and in situ stress measurement.
C. The long-term strength of rock under triaxle stress state was researched with the aid of laboratory testing results and in situ stress measurement.
Simanullang, I. L.*; Honda, Yuki; Fukaya, Yuji; Goto, Minoru; Shimazaki, Yosuke; Fujimoto, Nozomu*; Takada, Shoji
JAEA-Technology 2015-032, 26 Pages, 2016/01
Decay heat of the High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor had been evaluated by the Shure Equation and/or ORIGEN code based on the LWR's data. However, to evaluate more accurately, a suitable method must be considered because of the differences neutron spectrums from the LWRs. Therefore, the decay heat and the generated nuclides for the neutron spectrums of the core with different graphite moderator amount were calculated by the ORIGEN2 code. As a result, it is clear that the calculated decay heats are similar value with LWRs for about one year after the reactor shutdown, and that the significant differences are observed on the longer period affected by the generated nuclides such as  Y,
Y,  Cs,
Cs,  Pr,
Pr, 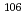 Rh,
Rh,  Am etc. It is also clear that the dose is affected by
Am etc. It is also clear that the dose is affected by  Pu on the initial stage after the reactor shutdown.
Pu on the initial stage after the reactor shutdown.
Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Sakamoto, Yoshifumi; Akai, Masanobu; Takazawa, Mayumi; Iida, Yoshihisa; Tanaka, Tadao; Nakayama, Shinichi
Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 32(1-7), p.298 - 310, 2007/00
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:72.78(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)Dissolution rate of montmorillonite, diffusivity of hydroxide ion and permeability coefficient in compacted sand-bentonite mixtures were experimentally determined and formulated. A coupled mass-transport/chemical-reaction code was developed to predict variation in permeability of engineered bentonite barrier with alkaline fluid by using the formulae.
Aiba, Nobuyuki; Tokuda, Shinji; Ishizawa, Tomoko*
Journal of Plasma Physics, 72(6), p.1127 - 1131, 2006/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:3.54(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)We develop the method for the stability analysis of a ideal external magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) mode by solving the eigenvalue problem associated with the two-dimensional Newcomb equation, the inertia free linear ideal MHD equation. This eigenvalue problem can be expected to provide a powerful tool for not only a low-n external MHD mode but also a high-n mode, where n is a toroidal mode number. With this method, we analyze an effect of the aspect ratio on the stability of middle-n (1 n
n 10) external MHD modes in tokamaks; this gets attention for the design research of a high performance tokamak. As the result of this work, we study that external MHD modes become stable as the aspect ratio decreases, and also find that the stability of middle-n external modes becomes important because an effect of a conducting wall is enhanced by reducing the aspect ratio.
10) external MHD modes in tokamaks; this gets attention for the design research of a high performance tokamak. As the result of this work, we study that external MHD modes become stable as the aspect ratio decreases, and also find that the stability of middle-n external modes becomes important because an effect of a conducting wall is enhanced by reducing the aspect ratio.
Nagashima, Yoshihiko*; Ito, Kimitaka*; Ito, Sanae*; Fujisawa, Akihide*; Hoshino, Katsumichi; Takase, Yuichi*; Yagi, Masatoshi*; Ejiri, Akira*; Ida, Katsumi*; Shinohara, Koji; et al.
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 48(4), p.S1 - S15, 2006/04
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:74.41(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)This paper presents the results of bispectral analysis of floating potential fluctuations in the edge region of ohmically heated plasmas in the JFT-2M tokamak. Inside of the outermost magnetic surface,coherent modes were observed around the frequency of geodesic acoustic mode which is a kind of the zonal flow. The squared bicoherence shows significant nonlinear couplings between the coherent fluctuations and the background fluctuations (which are likely to contain drift wave turbulent fluctuations). The experimental results that the total bicoherence is proportional to the squared amplitude of the coherent fluctuation, and that the biphase of the coherent modes localizes around a constant value  , are consistent with the theoretical prediction on the drift wave - zonal flow systems based on the Hasegawa-Mima model.
, are consistent with the theoretical prediction on the drift wave - zonal flow systems based on the Hasegawa-Mima model.
Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; Kudo, Yusuke; Tsuchiya, Katsuhiko; Kizu, Kaname; Ando, Toshinari*; Matsukawa, Makoto; Tamai, Hiroshi; Miura, Yukitoshi
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(8-14), p.1005 - 1011, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.14(Nuclear Science & Technology)This paper presents dependence of the stress intensity factor, around the defect in the butt joint welding of a superconducting conductor conduit, on a geometrical factor estimated by fracture mechanics analysis. The stress intensity factor can be estimated by the Newman-Raju equation about CICC section, but the effect of the difference between the geometry assumed in the equation and CICC has not been clarified yet. Therefore, the three-dimensional finite element method (3D-FEM) is performed to estimate the geometrical factor. As a result, the Newman-Raju equation is considered to be available for the assessment of the fracture toughness of the conduit of rectangular shape because the maximum stress intensity factor by 3-D FEM is only 3% larger than that by the Newman-Raju equation in the maximum postulated defect.
Takamatsu, Kuniyoshi; Nakagawa, Shigeaki
JAERI-Data/Code 2005-003, 31 Pages, 2005/06
Safety demonstration tests using the High Temperature engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) are in progress to verify the inherent safety features for High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactors (HTGRs). The coolant flow reduction test by tripping gas circulators is one of the safety demonstration tests. The reactor power safely brings to a stable level without a reactor scram and the temperature transient of the reactor-core is very slow. The TAC/BLOOST code was developed to analyze reactor and temperature transient during the coolant flow reduction test taking account of reactor dynamics. This paper describes the validation result of the TAC/BLOOST code with the measured values of gas circulators tripping tests at 30 % (9 MW). It was confirmed that the TAC/BLOOST code was able to analyze the reactor transient during the test.
Owaki, Hirokazu; Sugihara, Masayoshi; Kawano, Yasunori; Lukash, V. V.*; Khayrutdinov, R. R.*; Zhogolev, V.*; Ozeki, Takahisa; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*
Europhysics Conference Abstracts (CD-ROM), 29C, 4 Pages, 2005/00
no abstracts in English
Utsumi, Takayuki*; Kimura, Hideo
JSME International Journal, Series B, 47(4), p.761 - 767, 2004/11
In this paper, we show that a new numerical method, the Constrained Interpolation Profile - Basis Set (CIP-BS) method, can solve partial differential equations (PDEs) with high accuracy and can be a universal solver by presenting examples for the solutions of typical parabolic, hyperbolic, and elliptic equations. Here, we present the numerical errors caused by this method, and illustrate that the solutions by the CIP-BS method, in which fifth order polynomials are used to constrain the values and first and second order spatial derivatives, are highly refined compared to those by the CIP-BS
method, in which fifth order polynomials are used to constrain the values and first and second order spatial derivatives, are highly refined compared to those by the CIP-BS method, in which third order polynomials are used to constrain the values and first order spatial derivatives. The fact that this method can unambiguously solve PDEs with an one-to-one correspondence to analytical requirements is also shown for PDEs including singular functions like the Dirac delta function with Dirichet or Neumann boundary conditions. This method is straightforwardly applicable to PDEs describing complex physical and engineering problems.
method, in which third order polynomials are used to constrain the values and first order spatial derivatives. The fact that this method can unambiguously solve PDEs with an one-to-one correspondence to analytical requirements is also shown for PDEs including singular functions like the Dirac delta function with Dirichet or Neumann boundary conditions. This method is straightforwardly applicable to PDEs describing complex physical and engineering problems.
Utsumi, Takayuki*; Yabe, Takashi*; Aoki, Takayuki*; Koga, J. K.; Yamagiwa, Mitsuru
JSME International Journal, Series B, 47(4), p.768 - 776, 2004/11
no abstracts in English
Aiba, Nobuyuki*; Tokuda, Shinji; Ishizawa, Tomoko*; Okamoto, Masao*
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 46(11), p.1699 - 1721, 2004/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:9.95(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The theory of the Newcomb equation has been applied to low-n external modes in a tokamak and a method has been developed to compute the stability matrix that gives the change of plasma potential energy due to external modes in terms of the surface values of the perturbations. By using this method, the spectral properties of the ideal external modes has been elucidated, such as coupling between external modes and internal modes, and the difference of the stability properties between a normal shear tokamak and a reversed shear tokamak. These results will be also useful in the stability analysis of resistive wall modes.
Morishita, Takatoshi; Inoue, Takashi; Iga, Takashi*; Watanabe, Kazuhiro; Imai, Tsuyoshi
Review of Scientific Instruments, 75(5), p.1764 - 1766, 2004/05
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:42.73(Instruments & Instrumentation)Negative ion beams of high current density are required for accelerator and fusion. The H source utilizes surface production that produces H
source utilizes surface production that produces H from H or H
from H or H . And hence, high proto yield ion source is required. Generally, a large volume plasma generator with strong plasma confinement is suitable to achieve high proton yield. On the contrary, production of high proton ratio plasma is not easy in small sources. However, in a small source (3.5 liter), high current H
. And hence, high proto yield ion source is required. Generally, a large volume plasma generator with strong plasma confinement is suitable to achieve high proton yield. On the contrary, production of high proton ratio plasma is not easy in small sources. However, in a small source (3.5 liter), high current H beam of 800 A/m
beam of 800 A/m was obtained. In this research, the proton ratio was investigated experimentally and analytically in a small source (1.4 liter). The measured proton ratio increased form 40% to 90% by applying the magnetic filter. From the numerical analysis, the proton ratio is low as 40% in the driver region. However, with the magnetic filter, flow of primary electrons is restrained, resulting in suppression of H
was obtained. In this research, the proton ratio was investigated experimentally and analytically in a small source (1.4 liter). The measured proton ratio increased form 40% to 90% by applying the magnetic filter. From the numerical analysis, the proton ratio is low as 40% in the driver region. However, with the magnetic filter, flow of primary electrons is restrained, resulting in suppression of H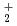 production at the extraction region. In addition, molecular ions are easily destroyed by thermal electrons in the filter region. Thus the proton ratio is enhanced by the magnetic field in the small sources.
production at the extraction region. In addition, molecular ions are easily destroyed by thermal electrons in the filter region. Thus the proton ratio is enhanced by the magnetic field in the small sources.